In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, securing online accounts has never been more crucial. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) offers an additional layer of security, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access. This article will explore the importance of 2FA, its working mechanism, its advantages and potential flaws, and how it compares to other security methods.Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to provide two different forms of identification before accessing an account or system. This adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a username and password.
The idea is to combine two factors from the following categories: Something You Know: This is usually a password or PIN. It’s information that only the user should know. Something You Have: This could be a physical object like a smartphone, a hardware token, or a smart card. In practice, this often involves receiving a code on a mobile device via SMS, a dedicated app (like Google Authenticator), or a hardware token generating a one-time passcode (OTP).Something You Are: This involves biometrics, such as a fingerprint, facial recognition, or voice recognition.
A typical 2FA process works as follows: The user enters their username and password. As a second step, they must verify their identity using the second factor, like entering a code sent to their phone or using a fingerprint scan.
By requiring two forms of authentication, 2FA makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, as they would need both the password and the second factor.
What’s the Difference Between Two-Step Verification and 2FA?
Two-step verification and 2FA are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Two-step verification requires two steps to authenticate a user, but these steps might not always involve two different factors. For example, entering a password and then answering a security question is two-step verification, but not 2FA, as both rely on “something you know.”
2FA, on the other hand, combines two of the following elements: “something you know” (password), “something you have” (a physical token or a smartphone), or “something you are” (biometrics like a fingerprint). This combination makes 2FA inherently more secure than two-step verification.
How is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) being used in the world?
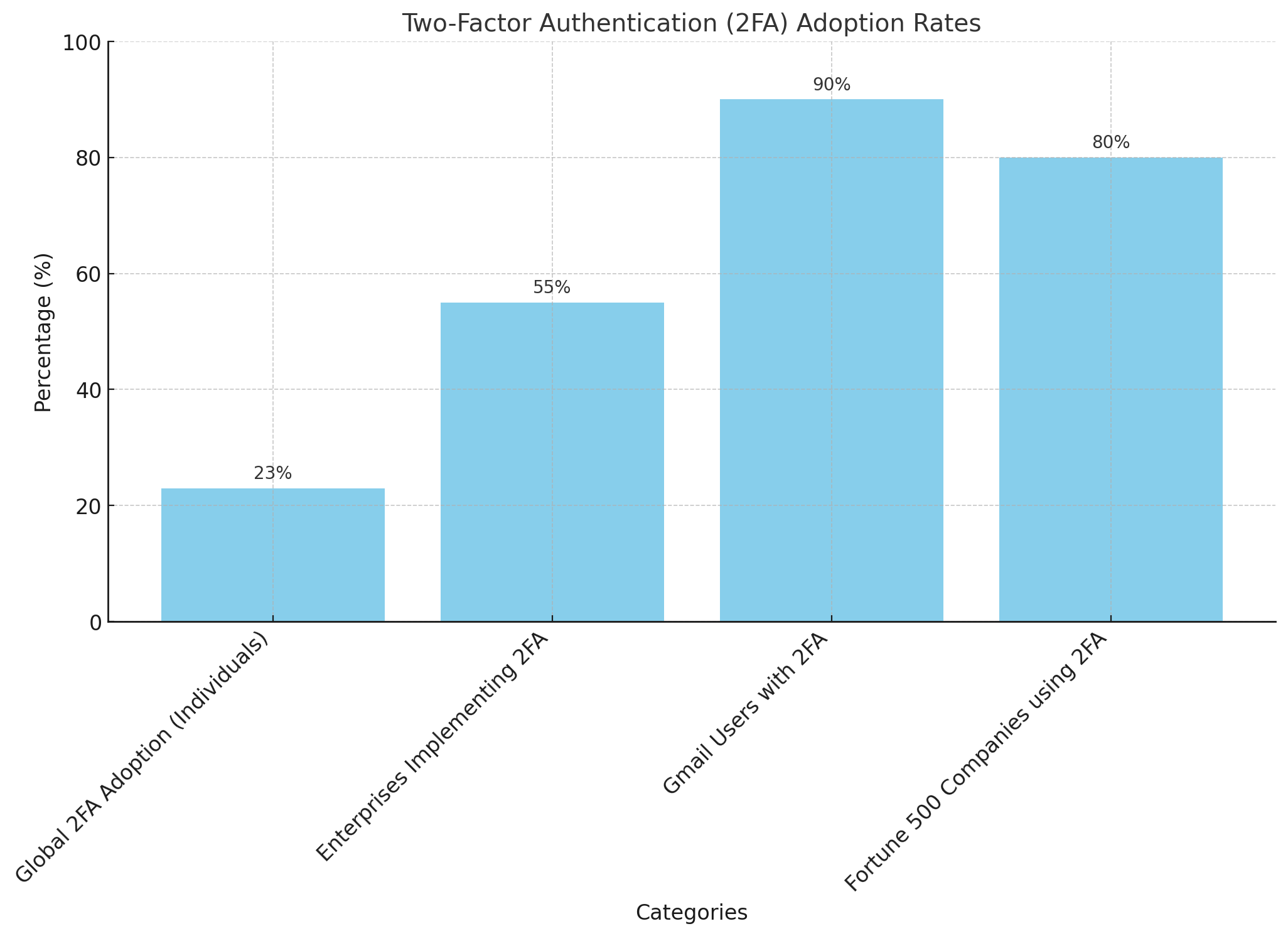
The bar chart illustrates the adoption rates of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) across various categories. While only 23% of individuals globally use 2FA for their online accounts, enterprises show a higher adoption rate, with 55% implementing or planning to implement 2FA. Among specific platforms, 90% of Gmail users have 2FA enabled, demonstrating a strong emphasis on security. Additionally, 80% of Fortune 500 companies use 2FA to protect employee accounts, highlighting its importance in securing sensitive data within large organizations. This data suggests a growing trend toward the adoption of 2FA, especially in corporate and platform-specific environments.
According to data taken from https://eftsure.com/, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) usage rates worldwide are as follows.
Common Types of Two-Factor Authentication Methods
2FA can be implemented using various methods, each with its own level of security and convenience. The most common methods include:
SMS Verification: A code is sent to the user’s mobile phone via SMS. While easy to use, it is vulnerable to SIM swapping and interception.
Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP). These codes are more secure than SMS as they are not transmitted over a network.
Hardware Tokens: Devices like YubiKey generate unique codes or connect via USB to authenticate users. They offer high security but can be inconvenient if lost or forgotten.
Biometric Authentication: Uses physical characteristics such as fingerprints or facial recognition. It provides a high level of security but raises privacy concerns and potential for false positives or negatives.
Push Notifications: The user receives a notification on their device and simply approves the login attempt. This method is user-friendly and secure against phishing.
How 2FA Prevents Cyber Attacks
2FA adds an additional layer of defense, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if a password is compromised. In the case of phishing attacks, where a hacker might trick users into giving away their passwords, 2FA provides an extra barrier. Without access to the second factor, the hacker is unable to gain entry. This makes 2FA particularly effective against common cyber threats like phishing, brute force attacks, and keylogging.
The Risks of Not Using Two-Factor Authentication
Not using 2FA leaves accounts more vulnerable to attacks. If a hacker gains access to a password, they can easily infiltrate the account, leading to data breaches, financial loss, and identity theft. The impact can be severe, especially for sensitive accounts such as banking, healthcare, and email, where personal and confidential information is stored.
Overcoming Common Challenges with Two-Factor Authentication
Implementing 2FA can present challenges, such as user resistance due to perceived inconvenience or the risk of losing access to the second factor (e.g., losing a phone). To mitigate these issues: Education: Inform users about the benefits of 2FA and how it enhances security. Backup Options: Provide alternative methods for authentication, such as backup codes or secondary email addresses. Usability: Choose 2FA methods that balance security and convenience, like push notifications or biometric authentication.
How to use Google Authenticator
Google Authenticator is an app that provides two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance the security of your accounts. It generates a time-based one-time password (TOTP) that you use in addition to your regular password when logging into a service.

The Future of 2FA: Evolving Technologies and Trends
As cyber threats evolve, so does 2FA technology. Emerging trends include:
Passwordless Authentication: Moving beyond passwords entirely by using biometrics or security keys as primary authentication methods.
Adaptive Authentication: Adjusts the level of authentication required based on the context of the login attempt, such as location or device used.
FIDO2 and WebAuthn: New standards that enable more secure, passwordless authentication methods using public-key cryptography.
These advancements aim to enhance security while improving user experience, making 2FA more seamless and robust.
2FA and User Convenience: Balancing Security and Usability
A major challenge with 2FA is finding the right balance between security and user convenience. While high-security methods like hardware tokens offer superior protection, they can be inconvenient. Conversely, easier methods like SMS verification are more user-friendly but less secure. Striking this balance involves choosing a 2FA method that offers sufficient security without overly complicating the user experience. For many, this might mean using an authenticator app or push notifications, which provide a good compromise between security and ease of use.
Comparing Two-Factor Authentication with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
While 2FA requires two factors for authentication, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) can involve more than two. MFA could include a combination of something you know, have, and are, making it more secure than 2FA alone. For instance, accessing a highly sensitive system might require a password (something you know), a fingerprint scan (something you are), and a hardware token (something you have).
MFA offers enhanced security but can be more cumbersome for users. It is often used in environments where the highest level of security is required, such as government agencies and financial institutions.
Where Are the Flaws in Two-Factor Authentication?
While 2FA significantly enhances security, it is not foolproof. Some potential flaws include:
SIM Swapping: Hackers can hijack a phone number to intercept SMS codes.
Phishing Attacks: Sophisticated phishing attacks can trick users into revealing their 2FA codes.
Social Engineering: Attackers might manipulate individuals into providing their second-factor information.
Despite these vulnerabilities, 2FA still provides a much higher level of security compared to password-only protection.
Two-Factor Authentication is a vital security measure that adds an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access. While not perfect, it significantly reduces the risk of cyber attacks by requiring two forms of verification. As technology advances, 2FA continues to evolve, incorporating more user-friendly and secure methods. Balancing security and convenience is key, and implementing 2FA is a critical step in safeguarding personal and sensitive information.
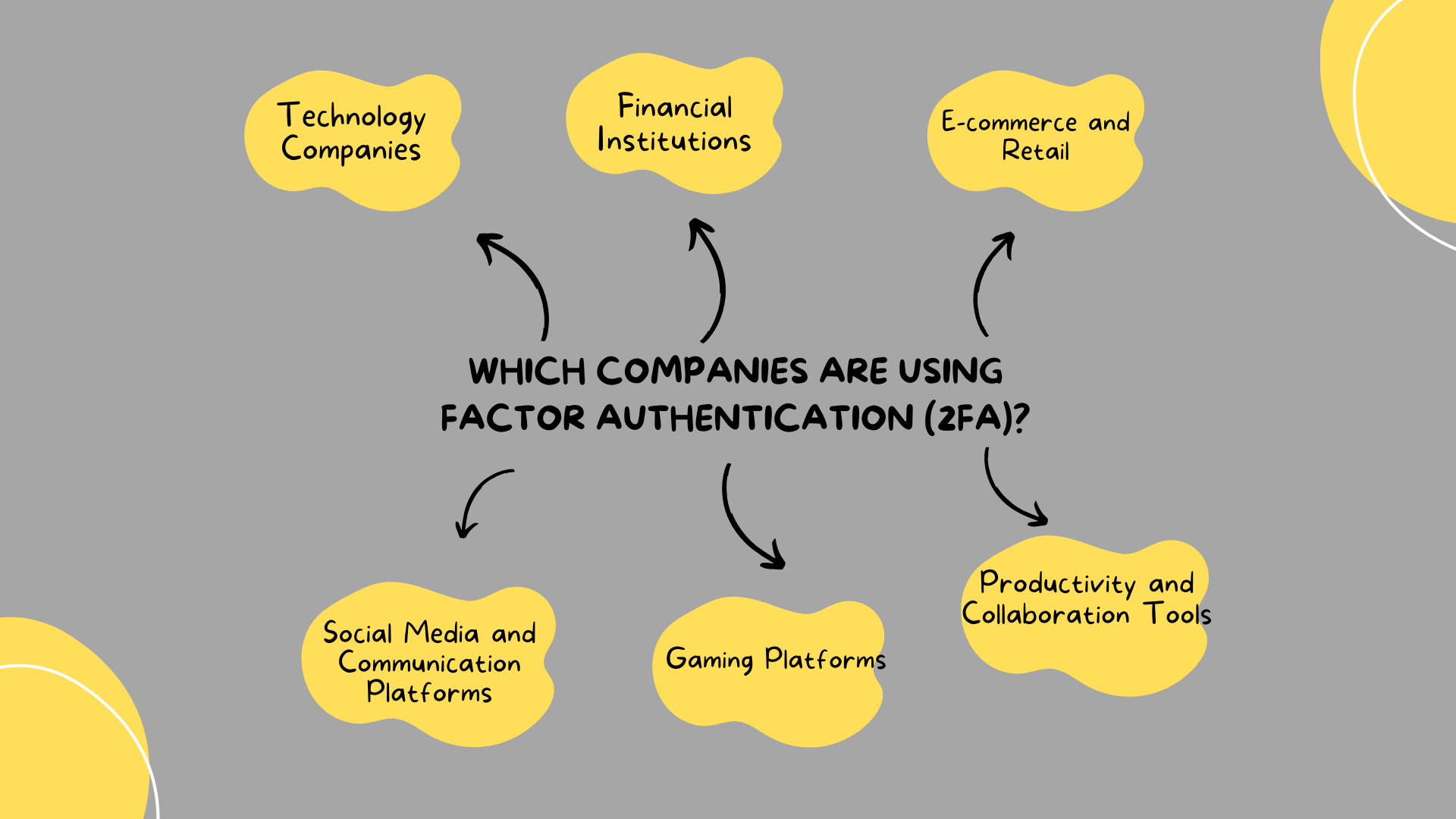
Which companies are using Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Many companies across various industries have adopted Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) as a standard security measure to protect user accounts and sensitive information. Here are some examples of companies and types of services that commonly use 2FA:
- Technology Companies
Google: Offers 2FA for Google accounts through various methods like Google Authenticator, SMS codes, and security keys.
Apple: Uses 2FA for Apple IDs to secure access to services like iCloud, iTunes, and the App Store.
Microsoft: Provides 2FA for Microsoft accounts, including services like Outlook, Office 365, and Xbox Live.
Amazon: Uses 2FA for Amazon accounts, including AWS (Amazon Web Services) accounts, offering SMS, app-based, and hardware key methods.
- Financial Institutions
Banks: Major banks such as Bank of America, Wells Fargo, Chase, and HSBC offer 2FA for online banking, including SMS codes, app-based authentication, and security questions.
PayPal: Uses 2FA to protect user accounts, offering SMS codes and app-based authentication methods.
Venmo: Provides 2FA for securing user accounts, primarily through SMS and authentication apps.
Credit Card Companies: Companies like American Express and Capital One offer 2FA options for online account management.
- E-commerce and Retail
Amazon: Offers 2FA for customer accounts to protect against unauthorized purchases and access to personal information.
eBay: Uses 2FA to secure customer accounts, offering SMS and app-based authentication.
Alibaba: Provides 2FA for its various services to enhance the security of user accounts.
- Social Media and Communication Platforms
Facebook: Implements 2FA for added security, using SMS codes, authentication apps, and physical security keys.
Instagram: Offers 2FA to protect user accounts, using SMS and authentication apps.
LinkedIn: Provides 2FA to secure professional profiles and account access.
WhatsApp: Uses 2FA to secure user accounts with a six-digit passcode.
Snapchat: Implements 2FA for user accounts, primarily through SMS-based codes and authentication apps.
- Email and Cloud Storage Services
Gmail: Google offers 2FA for Gmail through various methods, including Google Authenticator, SMS, and hardware keys.
Outlook: Microsoft provides 2FA for Outlook.com, securing access with SMS codes, app-based verification, and security keys.
Dropbox: Uses 2FA to protect user accounts, offering SMS codes and authentication apps.
OneDrive: Microsoft’s cloud storage service includes 2FA for account security.
- Gaming Platforms
Steam: Uses Steam Guard for 2FA, offering mobile app authentication and email codes.
PlayStation Network (PSN): Provides 2FA to protect user accounts through SMS and app-based codes.
Xbox Live: Microsoft uses 2FA for Xbox Live accounts, offering SMS, app-based authentication, and security keys.
Epic Games: Offers 2FA for its platform, including methods like email verification, SMS codes, and authenticator apps.
- Productivity and Collaboration Tools
Slack: Offers 2FA to secure workspace accounts, using SMS codes and authentication apps.
Zoom: Provides 2FA for user accounts to secure access to meetings and webinars.
Trello: Implements 2FA for user accounts, using app-based authentication.
GitHub: Uses 2FA to protect code repositories and accounts, offering SMS, authentication apps, and security keys.
- Healthcare and Insurance
Health Insurance Providers: Companies like Aetna, UnitedHealthcare, and Blue Cross Blue Shield use 2FA for online portals to secure personal health information.
Healthcare Portals: Services like MyChart and other patient portals use 2FA to protect patient records and appointment information.
- Government Services
IRS: The Internal Revenue Service offers 2FA for accessing online accounts, using methods like SMS codes and app-based verification.
Social Security Administration: Uses 2FA to secure access to online services and personal records.
- Education Platforms
University Portals: Many universities use 2FA to secure access to student and faculty portals, often using SMS, email codes, or authentication apps.
Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms like Canvas and Blackboard offer 2FA to protect educational resources and user accounts.
2FA has become a standard security practice across various industries to protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats. While the specific methods may vary, the adoption of 2FA helps ensure that even if passwords are compromised, there is an additional layer of security to safeguard sensitive information and user accounts.