In an increasingly digital world, ensuring security and protecting sensitive data is paramount. Traditional security methods like passwords and PINs, though widely used, are becoming less effective in the face of more sophisticated cyber threats. Biometric authentication, which relies on unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity, offers a robust alternative. This article explores how biometric authentication enhances security, examining its advantages, challenges, and future trends in cybersecurity.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that uses a person’s unique physical or behavioral traits to verify their identity. Common biometric identifiers include fingerprints, facial recognition, iris and retina scans, voice recognition, and behavioral biometrics such as typing patterns or gait. These characteristics are inherent to the individual, making them difficult to replicate or forge.
Biometric systems typically function through two stages: enrollment and recognition. During enrollment, biometric data is captured and stored in a secure database. When recognition is needed, the system compares the new data with the stored template to verify identity. This makes biometric authentication highly effective in both physical and digital security applications.
Key Advantages of Biometric Security Systems
Biometric authentication enhances security by providing unique and non-transferable identifiers. Unlike passwords, which can be stolen or forgotten, biometric traits are tied to an individual and are difficult to duplicate. This inherent uniqueness significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and identity theft.
Additionally, biometric systems offer convenience. Users do not need to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens. Simply presenting their biometric trait—whether a fingerprint or facial scan—grants access. This seamless experience improves user satisfaction while enhancing security.
Another advantage is the use of continuous authentication, particularly with behavioral biometrics. This method continuously monitors a user’s behavior, such as typing speed or mouse movements, ensuring the person interacting with the system remains the authorized user throughout the session.

Biometric Authentication vs. Traditional Passwords: Which is Safer?
Biometric authentication is generally considered safer than traditional passwords. While passwords are vulnerable to theft, brute-force attacks, and phishing, biometric traits are far more secure due to their uniqueness. A fingerprint or an iris scan cannot be easily guessed, shared, or replicated, making it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
Traditional passwords also face issues like reuse and poor management. Many users employ the same password across multiple platforms, increasing vulnerability if one account is compromised. Biometric systems eliminate this issue by linking access directly to the user’s physical characteristics, which are far more challenging to steal or spoof.
However, biometric systems are not without risks. If biometric data is compromised, it cannot be changed like a password. This makes data protection and encryption critical in ensuring the security of biometric systems.
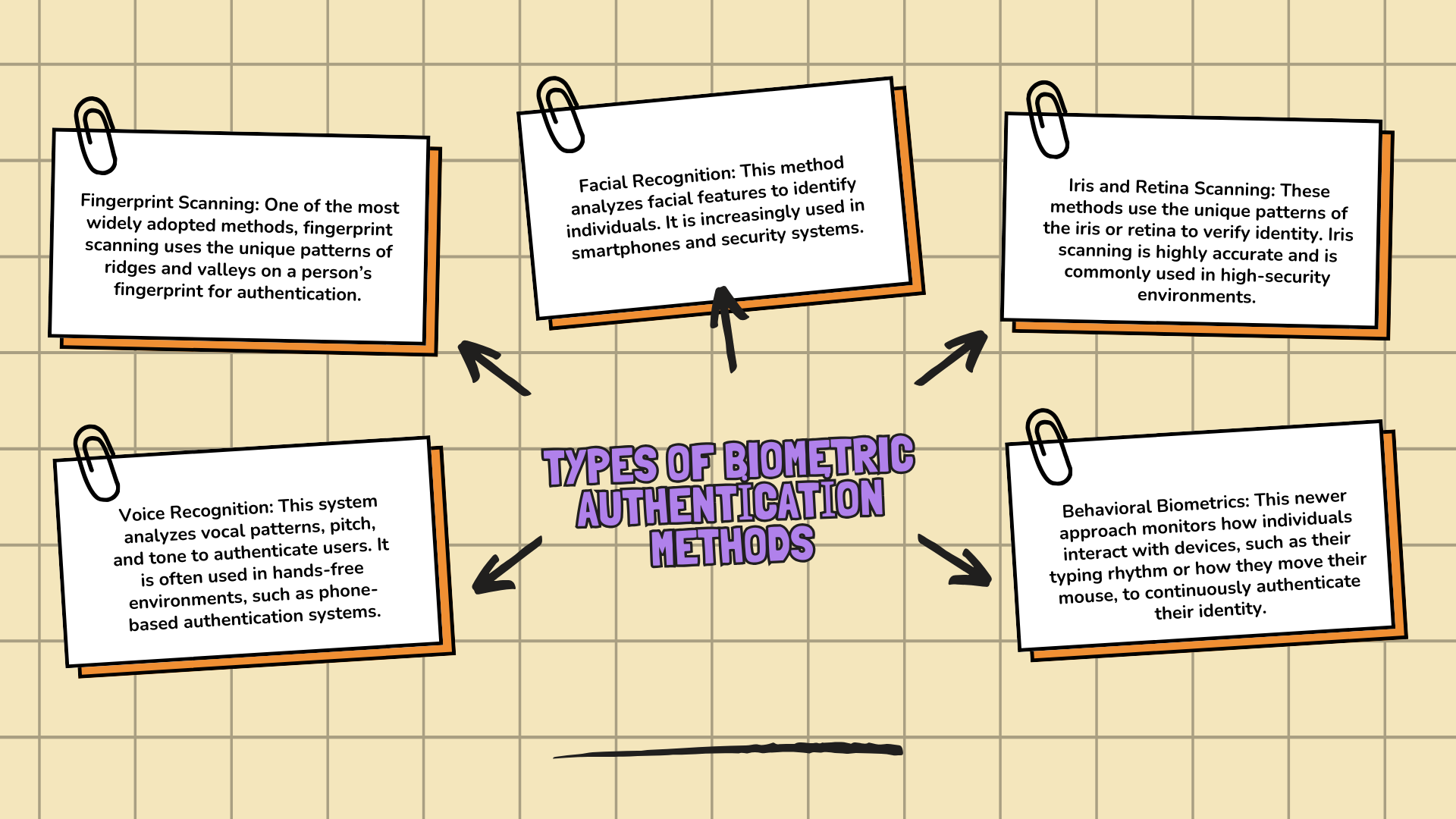
Types of Biometric Authentication Methods
Several biometric authentication methods are commonly used:
Fingerprint Scanning: One of the most widely adopted methods, fingerprint scanning uses the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on a person’s fingerprint for authentication.
Facial Recognition: This method analyzes facial features to identify individuals. It is increasingly used in smartphones and security systems.
Iris and Retina Scanning: These methods use the unique patterns of the iris or retina to verify identity. Iris scanning is highly accurate and is commonly used in high-security environments.
Voice Recognition: This system analyzes vocal patterns, pitch, and tone to authenticate users. It is often used in hands-free environments, such as phone-based authentication systems.
Behavioral Biometrics: This newer approach monitors how individuals interact with devices, such as their typing rhythm or how they move their mouse, to continuously authenticate their identity.
How Biometric Authentication Prevents Identity Theft
Biometric authentication significantly reduces the risk of identity theft. Since biometric data is unique to each individual, it is nearly impossible for a fraudster to replicate or steal these identifiers. Even if hackers gain access to personal information like social security numbers or passwords, they would still be unable to impersonate the individual without the corresponding biometric data.
Additionally, biometric systems can integrate with multi-factor authentication (MFA), where biometrics are combined with other verification methods such as passwords or tokens. This layered security approach adds extra protection, making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to bypass security protocols.
Challenges and Limitations of Biometric Security
Despite its advantages, biometric security systems face challenges. One key issue is accuracy. No biometric system is 100% foolproof—false positives (granting access to the wrong person) and false negatives (denying access to the correct person) can occur. External factors like lighting conditions, injuries, or even changes in a person’s appearance can affect system accuracy.
Another limitation is cost. Biometric systems, especially those requiring specialized hardware like iris scanners, can be expensive to implement and maintain. This can be a barrier for smaller organizations.
Finally, not everyone can be enrolled in biometric systems. Factors such as dark irises, vague fingerprints, or certain disabilities can make it difficult for some individuals to use these systems, potentially excluding them from accessing secure environments.
Biometric Data Privacy Concerns: How Safe Is Your Data?
Biometric data privacy is a significant concern. Unlike passwords, which can be changed if compromised, biometric traits are permanent. If biometric data is stolen, the individual is at risk of long-term identity theft. Therefore, organizations must ensure that biometric data is securely stored and encrypted.
Compliance with privacy regulations, such as GDPR, is also essential. Some regulations limit how biometric data can be collected, stored, and used. For instance, in some jurisdictions, biometric data cannot be stored in centralized databases and must be stored locally on the user’s device, reducing the risk of mass data breaches.
Usage rates of biometric authentication technology worldwide by sectors
The usage rates of biometric authentication technology worldwide according to sectors are as follows according to https://www.biometricsinstitute.org/ website data:
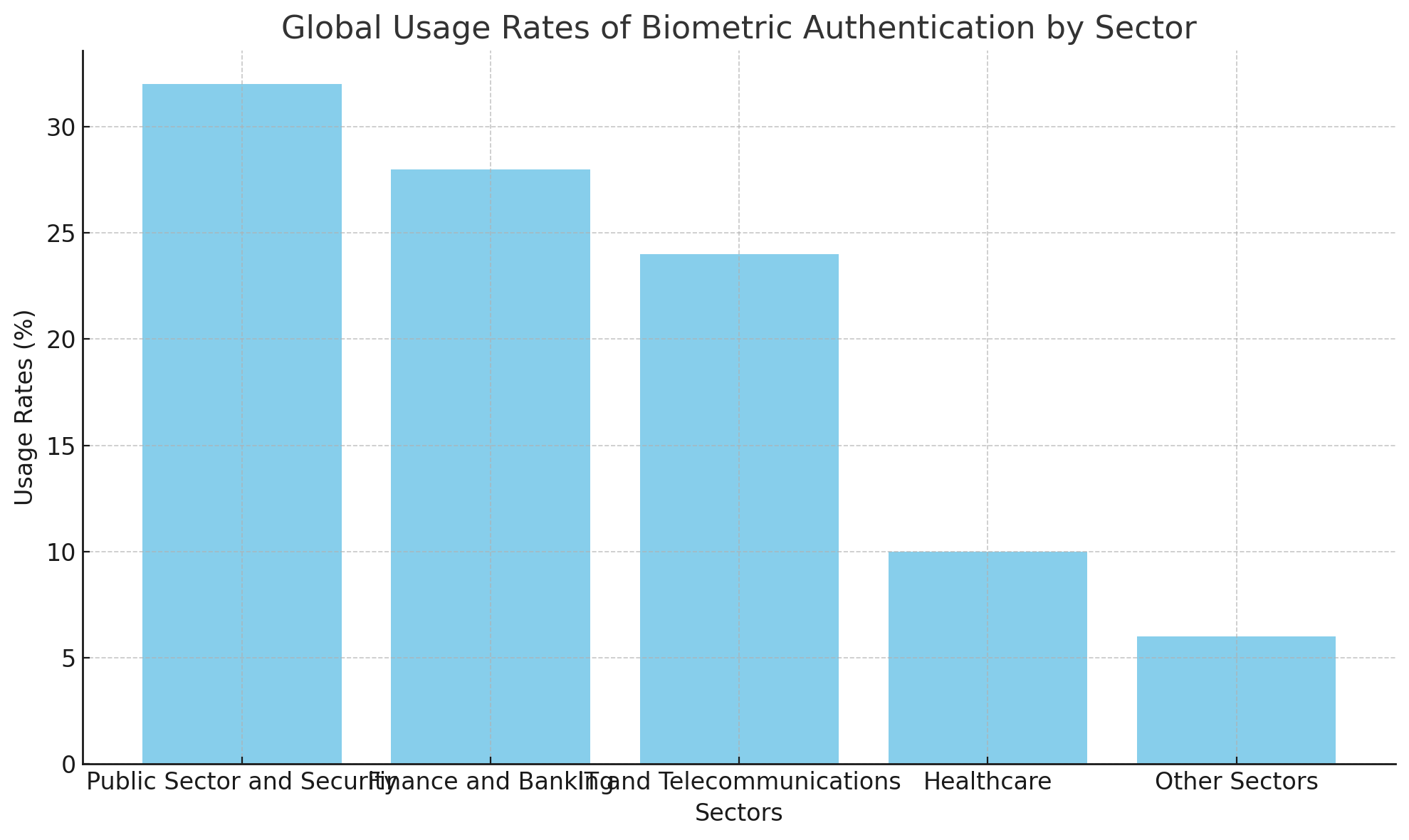
The chart above shows the global usage rates of biometric authentication technology by sector. As seen in the chart, the public sector and security have the highest biometric authentication usage at 32%, while the finance and banking sector ranks second with a usage rate of 28%. In the IT and telecommunications sector, the usage rate is 24%, while in the healthcare sector, it is 10%. Other sectors use biometric authentication at a rate of 6%. These data indicate that biometric technologies are concentrated, particularly in critical areas such as security, finance, and public services.
Applications of Biometric Security in Everyday Life
Biometric authentication is increasingly integrated into everyday life. Common applications include:
- Mobile Devices: Many smartphones use fingerprint or facial recognition to unlock devices and authorize payments.
- Banking: Financial institutions use biometrics to verify identity during transactions, reducing fraud in online banking.
- Healthcare: Biometrics are used to ensure the correct identification of patients, protecting their medical records and reducing errors.
Government and Law Enforcement: Governments employ biometric systems at border controls and in law enforcement to verify identities and enhance security.
Future Trends in Biometric Authentication Technology
The future of biometric authentication promises advancements in accuracy, accessibility, and security. Emerging trends include the development of multimodal biometric systems that combine multiple biometric traits, such as facial recognition and voice recognition, to enhance reliability.
Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are also improving biometric systems’ ability to detect sophisticated spoofing attempts. For example, 3D liveness detection can distinguish between a real person and a photo or video, providing greater security against fraud.
The Role of Biometrics in Enhancing Cybersecurity
In conclusion, biometric authentication plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity. By relying on unique physical and behavioral characteristics, biometric systems offer stronger security than traditional passwords. While challenges like data privacy, cost, and accuracy must be addressed, the benefits of biometrics in preventing identity theft, improving user convenience, and securing sensitive data are undeniable.
As biometric technology continues to evolve, it will likely become a fundamental component of cybersecurity strategies across various industries, offering a more secure and efficient way to protect digital identities and assets.
Several large companies across various industries have adopted biometric authentication as part of their security and access control systems. These companies utilize biometric technologies like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, iris scanning, voice recognition, and more to enhance security, streamline processes, and improve user experience. Here are some major global companies known for utilizing biometric authentication:
Apple: Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint (Touch ID) and facial recognition (Face ID). Usage: Apple introduced Touch ID with the iPhone 5S and later transitioned to Face ID with the iPhone X. Both technologies are integral to unlocking devices, authorizing app downloads, making payments via Apple Pay, and more.
Samsung: Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris scanning. Usage: Samsung uses these technologies across its Galaxy series of smartphones and tablets. They enable device unlocking, secure payment transactions (Samsung Pay), and other secure access functionalities.
Google: Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint and facial recognition. Usage: Google has implemented biometric authentication in its Pixel devices and within its broader ecosystem (e.g., Android). Fingerprint scanning and facial recognition are used for unlocking devices, authorizing transactions (Google Pay), and securing apps.
Microsoft: Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning. Usage: Microsoft’s Windows Hello offers biometric login options, including facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, for Windows devices. This allows secure access to devices and applications without the need for passwords.
Amazon: Biometric Technologies: Palm recognition, fingerprint scanning, voice recognition. Usage: Amazon introduced Amazon One, which uses palm recognition for secure payments and identification in retail environments. Amazon also integrates voice recognition through Alexa for secure access to accounts and sensitive operations.
Alibaba: Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning. Usage: Alibaba’s Alipay uses facial recognition for secure payments and account access. Their “Smile to Pay” technology allows users to make transactions simply by smiling at a camera.
Mastercard: Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint scanning, facial recognition. Usage: Mastercard has implemented biometric authentication in its payment systems, allowing users to verify their identity with fingerprints or facial recognition when making secure transactions.
Facebook (Meta): Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition and voice recognition. Usage: Facebook initially used facial recognition to tag people in photos but has expanded this to improve account security through identity verification. Voice recognition is also used to interact with Meta’s virtual assistant technologies.
Banking and Financial Institutions: Notable Companies: JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, Citibank, HSBC. Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, voice recognition, iris scanning. Usage: Banks and financial institutions are significant adopters of biometrics for user authentication, secure mobile banking, and fraud prevention. For example, Wells Fargo allows customers to access accounts through facial recognition or fingerprint scanning, while HSBC has implemented voice recognition for customer service.
Airlines: Notable Companies: Delta Air Lines, British Airways, Lufthansa. Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition, fingerprint scanning. Usage: Airlines use biometric authentication at various touchpoints, such as airport check-in, boarding, and security clearance. For instance, Delta and British Airways have introduced biometric boarding that allows passengers to board flights using facial recognition without a physical boarding pass.
Retail Giants: Notable Companies: Walmart, Whole Foods (Amazon-owned). Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition, palm recognition. Usage: Walmart has explored facial recognition technology for both security and customer experience purposes, while Whole Foods (owned by Amazon) uses Amazon One’s palm recognition system for contactless payments.
Government and Public Sector: Notable Countries: United States, China, India (Aadhaar system), UAE. Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint scanning, iris scanning, facial recognition. Usage: Governments use biometric authentication for national ID programs, border control, law enforcement, and public services. India’s Aadhaar system, the world’s largest biometric ID system, uses fingerprint and iris scans for identity verification in various public and private services.
Tesla: Biometric Technologies: Fingerprint and facial recognition (under development). Usage: Tesla has been exploring biometric authentication for future enhancements to vehicle security, including potential fingerprint and facial recognition systems for accessing and operating cars.
Tencent: Biometric Technologies: Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning.
Usage: Tencent, one of China’s largest technology companies, uses biometric authentication for its WeChat Pay platform, allowing users to make secure payments using facial or fingerprint recognition.
Biometric authentication is growing rapidly across industries, especially in tech, finance, retail, and government sectors. Leading companies like Apple, Samsung, and Google have played significant roles in popularizing biometric security features, while industries like banking, airlines, and retail have increasingly integrated these technologies to improve user experience and enhance security. As biometric systems continue to evolve, more companies are likely to adopt them, making them a cornerstone of future digital authentication methods.