Establishing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on your home network can provide numerous benefits, including enhanced privacy, secure internet browsing, and access to geographically restricted content. This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of setting up a VPN, from understanding what a VPN is and why you might need one, to choosing the right service and configuring it on your home network.
Understanding a VPN and Its Importance at Home
A VPN is a service that encrypts your internet connection and routes it through a secure server, effectively masking your IP address and keeping your online activities private. When you use a VPN, your data is sent through an encrypted tunnel, which prevents others, such as your Internet Service Provider (ISP), hackers, or government agencies, from monitoring your internet traffic.
What are the vpn usage rates around the world?
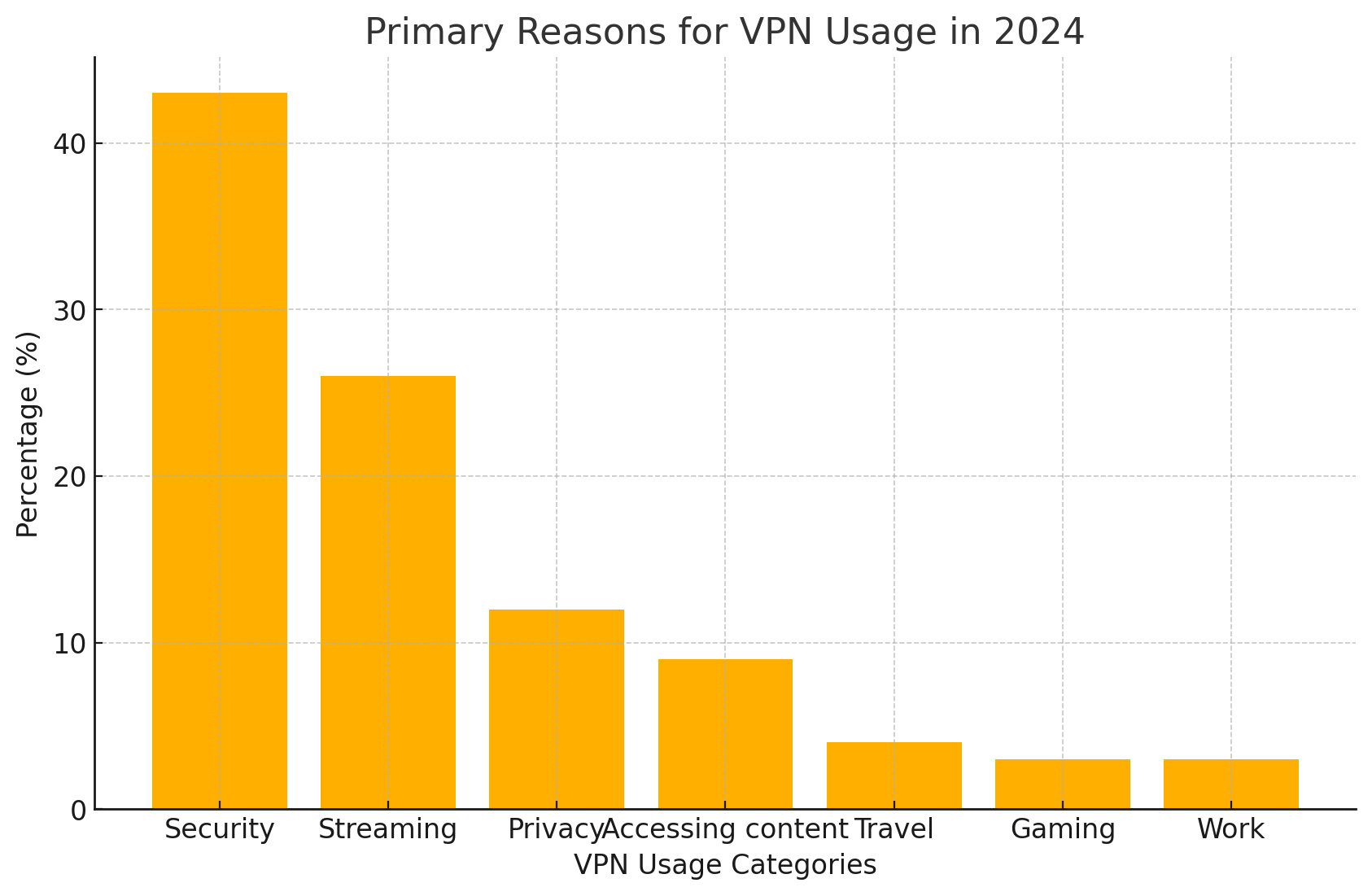
The bar chart illustrates the primary reasons for VPN usage in 2024. Security is the most common reason, accounting for 43% of VPN use, indicating a strong focus on protecting personal and sensitive information online. Streaming services follow, with 26% of users employing VPNs to access geographically restricted content, such as movies and TV shows. Privacy concerns motivate 12% of users to utilize VPNs, seeking to maintain anonymity while browsing. A smaller percentage of users employ VPNs for accessing specific content (9%), travel-related needs (4%), gaming (3%), and work purposes (3%). This distribution highlights the growing importance of online security and unrestricted access in today’s digital landscape.
According to the data taken from https://www.forbes.com/ and https://www.statista.com/, vpn usage rates worldwide are as follows.
Why Use a VPN at Home?
Using a VPN at home can offer several key benefits:
Privacy Protection: ISPs often track and log users’ browsing activities. A VPN hides your internet traffic, ensuring your online activities remain private and secure.
Access to Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to connect to servers in different countries, enabling you to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that may not be available in your region.
Enhanced Security: Even at home, your network can be vulnerable to cyber threats. A VPN adds an extra layer of encryption, protecting your data from potential breaches.
Choosing the Right VPN for Your Home
Selecting an appropriate VPN is crucial to ensure it meets your specific needs. Consider the following factors when choosing a VPN service:
Encryption Standards: Look for a VPN that uses strong encryption methods like AES-256 to secure your data.
Server Network: A VPN with a broad network of servers across various countries provides better options for accessing content and ensuring a stable connection.
No-Log Policy: Ensure the VPN provider adheres to a strict no-log policy, meaning they don’t keep records of your online activities.
Connection Speed: Choose a VPN known for high-speed servers to minimize any impact on your internet connection.
Preparing Your Home Network for VPN Setup
Before you proceed with setting up a VPN, ensure that your home network is properly secured:
Router Security: Change the default username and password on your router to prevent unauthorized access.
Firmware Updates: Regularly update your router’s firmware to protect against security vulnerabilities.
Wi-Fi Encryption: Use WPA3 encryption on your Wi-Fi network to safeguard against unauthorized access.
Exploring Advanced VPN Features
Modern VPNs offer advanced features that can enhance your online experience:
Split Tunneling: Allows you to choose which applications or websites use the VPN connection while others use your regular internet connection. This is useful for optimizing speed and accessing local network devices while still maintaining security.
Kill Switch: A kill switch automatically disconnects your internet if the VPN connection drops, ensuring that your data is not exposed during an unexpected disconnection.
Multi-Hop: Some VPNs offer the option to route your traffic through multiple servers, adding an additional layer of anonymity.
Setting Up a VPN on Your Router
Configuring a VPN directly on your router secures all devices connected to your network. Here’s how to do it:
Check Router Compatibility: Verify that your router supports VPN installation. Some routers come with built-in VPN functionality, while others may require third-party firmware such as DD-WRT or Tomato.
Access Router Settings: Log into your router’s admin panel, usually accessible via a web browser. You’ll need the router’s IP address and login credentials.
VPN Configuration: Enter the VPN configuration details provided by your VPN service, including server addresses and your login credentials.
Testing: Once configured, test your VPN connection by checking your IP address online to ensure it matches the VPN server’s location.
Creating a VPN Server on Your Computer or NAS
For a more hands-on approach, you can create your own VPN server using a computer or a Network Attached Storage (NAS) device:
Using Built-In Tools: Windows and macOS offer built-in tools to set up a VPN server, though this requires some technical know-how. For instance, you can use the “Incoming Connections” feature in Windows or the “Remote Login” feature in macOS.
NAS Devices: Many NAS devices, like Synology or QNAP, offer VPN server capabilities. This method is useful for creating a secure connection to your home network while you’re away.
Port Forwarding: To access your home VPN server remotely, set up port forwarding on your router to direct VPN traffic to the appropriate device.
Testing Your VPN Connection
After setting up your VPN, it’s essential to verify that it’s working correctly:
Verify IP Address: Use an IP lookup service to confirm that your public IP address reflects the VPN server’s location.
Check for Leaks: Use online tools to test for DNS, IP, and WebRTC leaks to ensure your real IP address and other identifying information are not exposed.
Evaluate Connection Speed: Conduct an internet speed test to determine if the VPN is affecting your connection performance.
Staying Legal and Safe While Using a VPN
While VPNs offer enhanced privacy and security, it’s important to use them legally and responsibly:
Compliance with Terms of Service: Be aware of and adhere to the terms of service of both the VPN provider and the websites you visit.
Avoid Illegal Activities: Using a VPN does not provide immunity from the law. Always ensure that your online activities are legal and ethical.
Trustworthy VPN Providers: Use reputable VPN services to avoid providers that might log your data or expose you to security risks.
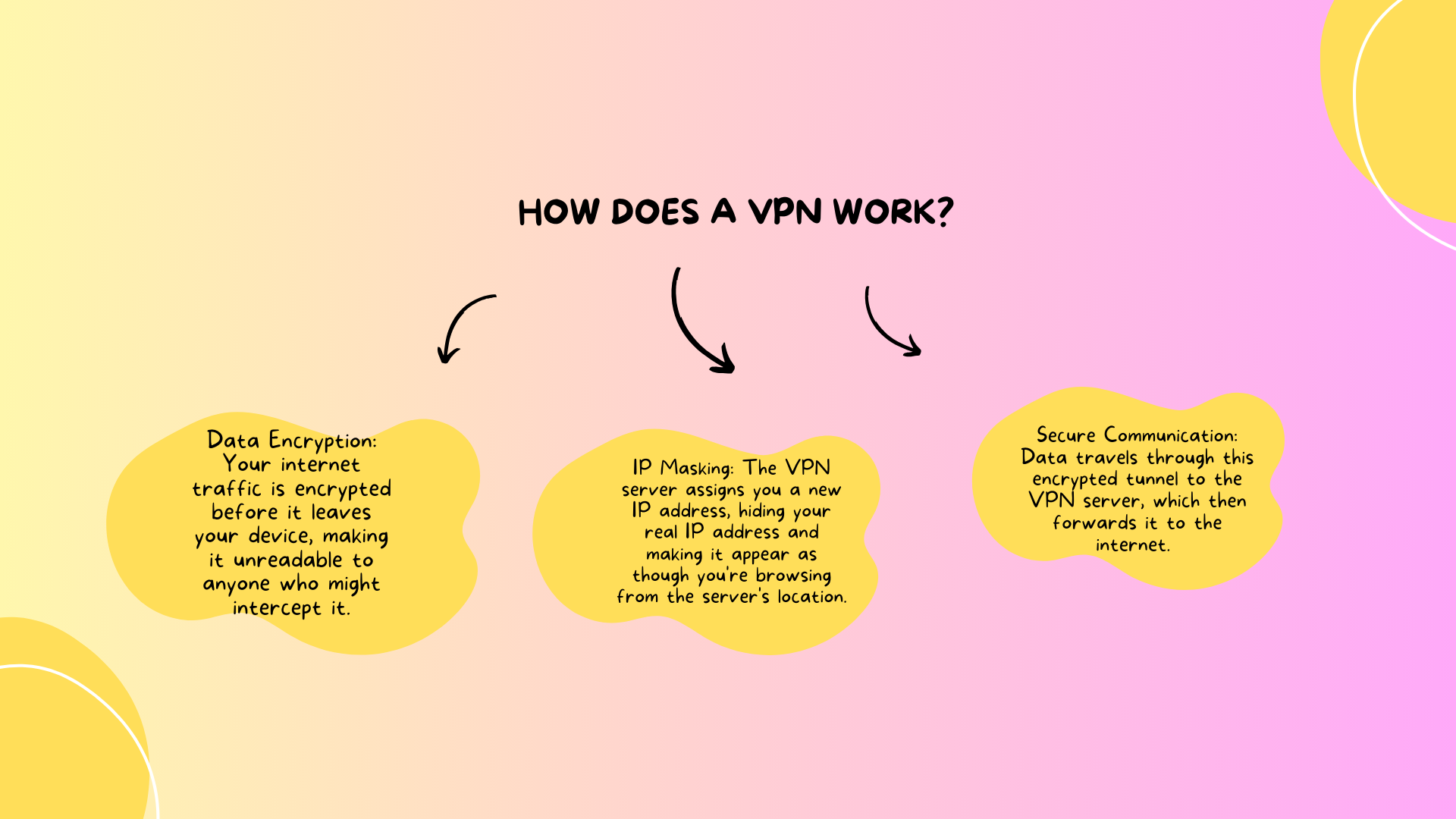
How Does a VPN Work?
A VPN works by creating a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server operated by the VPN provider. When you connect to the internet through a VPN:
Data Encryption: Your internet traffic is encrypted before it leaves your device, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it.
IP Masking: The VPN server assigns you a new IP address, hiding your real IP address and making it appear as though you’re browsing from the server’s location.
Secure Communication: Data travels through this encrypted tunnel to the VPN server, which then forwards it to the internet. This process makes it difficult for ISPs, hackers, or other entities to monitor your online activities.
What are the companies using Vpn?
Many companies use VPN services for various reasons, including data security, secure access for remote employees, bypassing geographical restrictions, and encrypting data. Here are some sectors and companies that use VPNs:
Technology Companies: Google: Uses VPNs to ensure secure access for employees to internal systems. Microsoft: Utilizes VPNs particularly for remote workers and secure data transfer.
Finance and Banking: JPMorgan Chase: Uses VPNs to ensure the security of financial data. Goldman Sachs: Employs VPN services due to high security requirements.
E-commerce: Amazon: Uses VPNs for secure access for employees and to bypass content restrictions in certain regions. eBay: Utilizes VPN services for secure data transfer and the protection of user information.
Healthcare Sector : Mayo Clinic: Uses VPNs to ensure the privacy and security of patient data.
Cleveland Clinic: Utilizes VPN services for secure remote access for doctors and staff.
Media and Entertainment: Netflix: Uses VPNs to manage regional restrictions and ensure secure access for employees.: Disney: Employs VPN services in content production processes and for secure employee access.
Gaming Companies: Electronic Arts (EA): Uses VPNs to ensure secure operations for development teams and to bypass geographical restrictions. Ubisoft: Utilizes VPN services to ensure secure access for global teams.
Consulting and Professional Services: Deloitte: Uses VPNs to ensure the security of client data.
Accenture: Benefits from VPN services for the security of global teams and client information.
These companies use VPNs for various purposes, such as allowing secure remote access to the company network, encrypting data, and bypassing geographical restrictions. Particularly in recent years, with the increase in remote work trends, VPN usage has become widespread among companies.
Setting up a VPN on your home network is a straightforward process that significantly enhances your online security and privacy. Whether you choose to install a VPN on your router, create your own server, or use a VPN service on individual devices, the key is to select a reliable provider and configure it correctly. With a VPN in place, you can enjoy a more secure and private internet experience, free from unwanted tracking and access restrictions.