SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are encryption protocols that provide secure data transmission over the internet. These technologies establish a secure connection between the web browser and server, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. This connection process begins with a series of security steps known as the “handshake.” During this process, encryption type and keys are determined, ensuring data privacy during transmission. This way, data is encrypted and shared only between the two communicating parties, preventing third parties from accessing it.
What Are the Differences Between SSL and TLS?
SSL and TLS function similarly but differ in security levels. SSL was initially developed as the first standard protocol for internet security, but due to security vulnerabilities, it has been replaced by the more advanced TLS. TLS addresses SSL’s shortcomings, offering stronger encryption algorithms and is currently the most widely used version. For instance, TLS 1.3 provides new features that enable faster connection times and enhanced security. Although many users still use the term “SSL,” what is used today is actually TLS.
How Does SSL/TLS Encryption Ensure Online Security?
SSL/TLS encryption ensures that data is encrypted before being transmitted over the internet. This means that user information can only be read by the sender and receiver. With encrypted data, the risk of unauthorized access to private and financial data during online transactions is minimized. In short, SSL/TLS encryption allows users to securely transmit data in an online environment.
Why Is It Necessary to Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate?
SSL/TLS certificates are digital documents that verify a website’s identity and act as a security indicator for users. Websites with these certificates are displayed with the HTTPS protocol and a lock symbol in the browser. These symbols help users understand that the site is secure and that they can safely share their information. Therefore, obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate is essential for ensuring user security and creating a secure online platform.
The Importance of SSL/TLS Encryption for E-Commerce
E-commerce sites are responsible for safeguarding users’ sensitive data, such as payment information. SSL/TLS encryption makes private data, like credit card information, secure and reduces the risk of data theft. Users feel safer when making transactions on a secure e-commerce site, which increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. A secure infrastructure also enhances brand reputation and increases the likelihood of users returning to the site.
Risks You May Face Without SSL/TLS Encryption
Sites without SSL/TLS encryption face significant security threats. Sensitive data, especially financial or personal information, can easily be compromised without this security protocol. Unencrypted data transmission carries the risk of phishing, data leakage, and brand reputation damage. Sites that fail to protect user information can experience long-term trust issues and risk losing their users.
How to Identify if a Website is Secure: SSL and HTTPS Tips
One of the simplest ways to determine if a website is secure is to check for the HTTPS protocol and lock symbol in the browser. HTTPS indicates that a secure connection has been established, and this connection is verified by an SSL/TLS certificate. Additionally, users can verify the certificate’s validity and whether it was issued by a reputable authority to further confirm the site’s security. These security indicators assure users that data is encrypted and safe.
How Does SSL/TLS Encryption Protect Against Data Theft and Phishing?
SSL/TLS encryption ensures that data is encrypted during transmission, meaning that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be meaningfully used by malicious actors due to its encrypted format. Additionally, SSL/TLS prevents phishing attacks by protecting users from being directed to fake sites. This contributes to a safer online experience, giving users confidence in their online transactions.
Best SSL/TLS Practices for E-Commerce Sites
For effective SSL/TLS usage on e-commerce sites, using the latest TLS version, obtaining certificates from a trusted authority, and regularly updating certificates is essential. Also, ensuring that all pages are accessible via HTTPS provides users with complete security. These practices are critical steps in maximizing security for e-commerce sites.
Which Websites Should Have SSL/TLS Certificates?
All websites that need to ensure data security in the online environment should use SSL/TLS certificates. Specifically, e-commerce sites, financial institutions, healthcare providers, and platforms processing user information must have these certificates. SSL/TLS certificates not only protect user security but also play a key role in maintaining company reputation.
What Kind of Data Does SSL/TLS Encryption Protect?
SSL/TLS protocols secure sensitive data such as usernames, passwords, and credit card information, as well as personal and financial information. For example, information transmitted during a payment transaction on an online shopping site is encrypted with SSL/TLS and can only be accessed by authorized parties. This ensures that users’ personal information remains secure and forms the foundation of data security.
What is the Difference Between SSL/TLS Encryption and Firewalls?
While SSL/TLS encryption ensures that data is transmitted in an encrypted manner, firewalls work by controlling network traffic to block potential threats. Firewalls detect unauthorized access and threats on the network, while SSL/TLS ensures that data is transmitted confidentially. These two security elements work together to provide a high level of online security.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates and Methods for Choosing the Right Certificate
SSL/TLS certificates are categorized according to validation types. Domain-validated (DV), organization-validated (OV), and extended-validation (EV) certificates are chosen based on security needs. DV certificates offer basic security, OV adds a security layer by verifying company identity, while EV provides the highest level of security and is particularly preferred for financial or high-security sites.
In conclusion, SSL/TLS encryption technology is a crucial component for securing online transactions. Secure connections protect user security and data privacy, creating a trustworthy digital platform. SSL/TLS is an indispensable security element for sectors handling sensitive information, like e-commerce and finance, playing a significant role in enhancing customer trust.
Which companies around the world use SSL/TLS?
Companies worldwide that use SSL/TLS encryption are spread across a broad spectrum, and almost all major security-focused digital platforms use SSL/TLS. Technology giants lead the sectors that actively use these encryption protocols. For instance, Google uses SSL/TLS protocols across all its services to protect user data, making this security the default in 2014. Apple also secures its users’ data by using SSL in services like iCloud and Apple Pay, while Microsoft ensures data security on platforms like Outlook, Microsoft 365, and Azure by using the SSL/TLS protocol. Facebook (Meta), on the other hand, uses SSL/TLS across all its social media platforms, especially to secure user accounts and messaging.
In addition to technology companies, e-commerce companies also stand out with their use of SSL/TLS. Amazon, one of the largest e-commerce platforms in the world, uses SSL across all its pages, providing high security especially in payment transactions. eBay uses SSL encryption to secure transactions between buyers and sellers, while Alibaba also utilizes SSL/TLS protocols to offer a secure shopping experience. In the financial services and banking sector, PayPal actively uses SSL encryption to ensure security in online payments, while Visa and Mastercard require SSL/TLS encryption for online credit card transactions in line with PCI-DSS standards. Many banks, such as JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, and ING, also use SSL/TLS in digital banking transactions to protect customer privacy.
The healthcare and insurance sectors also widely use SSL/TLS encryption. UnitedHealth Group uses SSL to protect the privacy of healthcare data, while insurance companies like Cigna and Aetna use SSL encryption to secure their customers’ personal health information. Epic Systems, which provides large data management platforms in the healthcare sector, also uses SSL. In the media and entertainment sector, companies benefit from SSL/TLS encryption. Netflix uses SSL to protect user information, payments, and viewing data, while Spotify ensures the security of user accounts and the privacy of music streaming data with SSL/TLS encryption. Hulu and Disney+ also use SSL encryption to protect user security.
Among cloud service providers, major names such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer SSL/TLS encryption to ensure data security. Additionally, government agencies in many countries use SSL encryption during online transactions. For example, the IRS and Social Security Administration in the United States use SSL to secure tax and social security transactions. Similarly, e-government portals in many countries, including Turkey, Germany, and Canada, are protected by SSL encryption.

These companies and sectors use SSL/TLS encryption extensively to protect the security and privacy of user data, establishing the SSL/TLS protocol as a security standard in situations where financial information, personal health data, and user information need to be protected.
What are the worldwide adoption rates of SSL/TLS?
According to the data on https://www.ssldragon.com/blog/ssl-stats/ and https://serpwatch.io/blog/ssl-stats/, SSL/TLS usage rates worldwide are as follows:
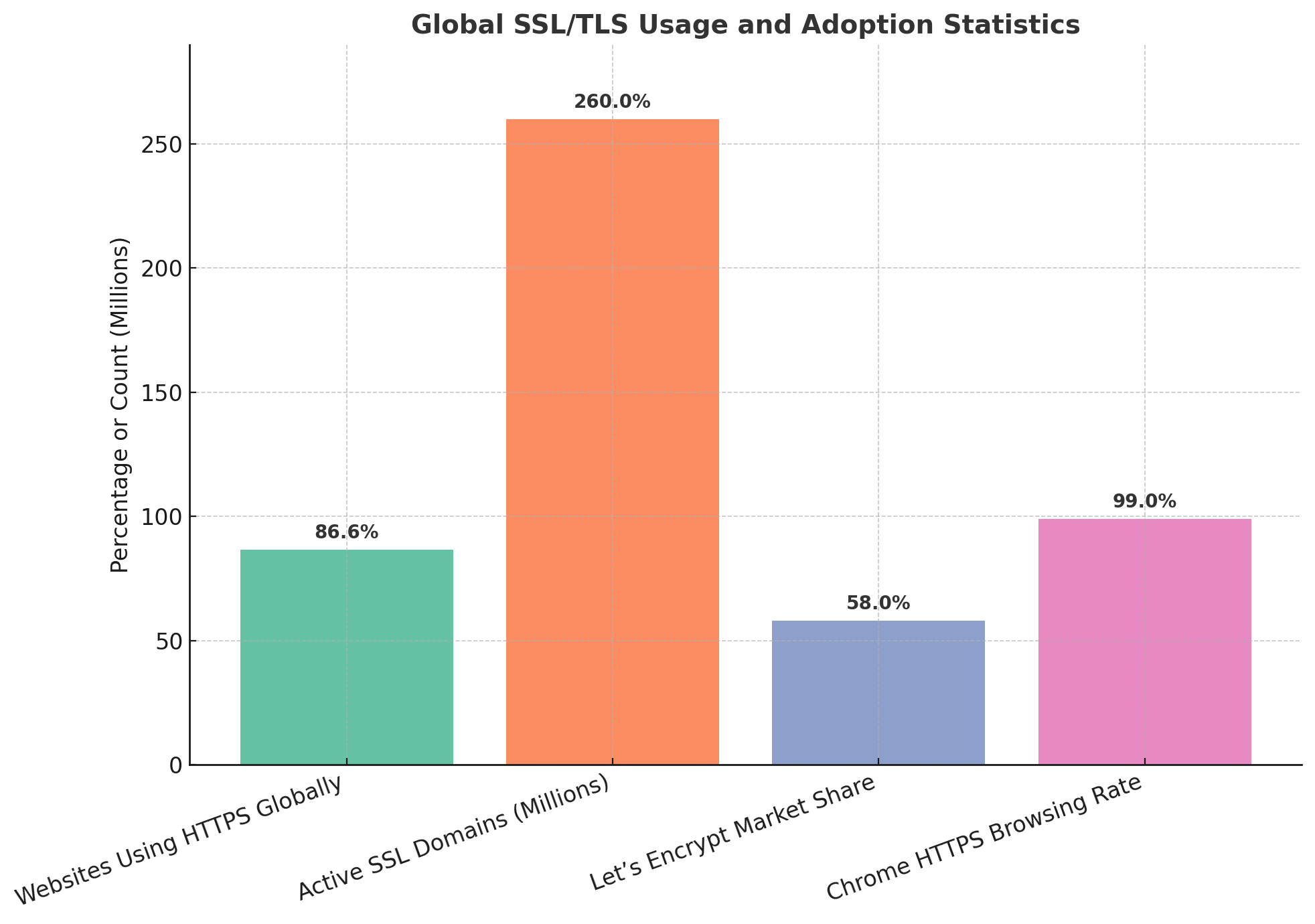
The global usage of SSL/TLS has been increasing each year, establishing itself as a fundamental element of internet security. Recent data shows that 86.6% of websites worldwide currently use the HTTPS protocol, with this rate continuously rising. Due to widely available free certificate providers like Let’s Encrypt, as of 2023, there are over 260 million active domains using SSL certificates globally. Let’s Encrypt holds more than 58% of the market share, followed by other key providers such as DigiCert and Sectigo. Analysis on the Chrome browser reveals that 99% of all web browsing is conducted over HTTPS, underscoring the impact of security standards promoted by major platforms like Google and Microsoft. In summary, SSL/TLS protocols are widely adopted worldwide, with the majority of websites utilizing HTTPS to secure visitor data.




