Cyberattacks are a serious threat in today’s world, affecting both individuals and businesses. These attacks on networks can lead to the theft of sensitive information, disabling systems, and significant financial losses. Therefore, ensuring network security should be a top priority for any organization. In this article, detailed information will be provided about the strategies you can apply, the tools you can use, and the threats you may encounter to protect your network.
What Cyber Threats Might You Face?
Cyber threats come in various forms, each with a different potential for harm. Common threats include:
- Malware: Malicious software like viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware can infiltrate your network, corrupt files, or steal your information.
- Phishing Attacks: These attacks aim to steal personal information, usually through fake emails or messages. They often succeed when employees unknowingly click on a link or share information.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt services by overwhelming your systems with excessive traffic.
- Social Engineering: These attacks aim to gain sensitive information by winning the trust of individuals. They often target employees to obtain passwords or user credentials.
Being aware of these threats and knowing that each one requires different defense mechanisms is the first step to creating an effective security strategy.
10 Important Steps to Protect Your Network
Implement a Strong Password Policy: Having long and complex passwords makes it harder for attackers to infiltrate your network. Additionally, regularly changing passwords enhances security.
Data Backup: Regular backups allow you to recover critical information in the event of an attack or data loss. Cloud-based backup solutions minimize the risk of data loss.
Use Antivirus and Antimalware Software: Using advanced antivirus and antimalware software to protect your computers from malicious software is crucial. These programs detect harmful software and block it from accessing your network.
Regular Software Updates: Keeping your systems and software up to date closes known security vulnerabilities. Older versions with unpatched flaws can be easy targets for cyber attackers.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): In cases where a single password is insufficient, MFA adds an extra layer of security. This method requires a second verification step when logging into systems.
Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your network traffic, especially when working remotely or accessing public networks, ensuring a secure connection. This protects your data from unauthorized access.
Firewalls and Advanced Network Monitoring: Firewalls prevent external threats from infiltrating the network, while network monitoring tools detect potential anomalies. A firewall filters incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking potential threats.
Network Segmentation: Dividing critical systems and data into separate segments makes it harder for attackers to take over the entire network. Network segmentation enhances security by limiting access to sensitive information.
Provide Security Training for Employees: Employee awareness is one of the most effective measures against cyberattacks. Training employees on threats like phishing attacks ensures they act with caution.
Use Data Encryption: Encrypting all data on the network ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable. Especially encrypting sensitive information minimizes the impact of data leaks.
How to Recognize and Prevent Phishing Attacks
Detecting phishing attacks requires vigilance. They often occur through emails, links directing to fake websites, or documents that appear legitimate but are fake. To prevent phishing attacks, use email filters, train employees on how to identify these types of attacks, and be cautious of messages from unknown sources. Additionally, conducting phishing tests helps measure employee awareness and strengthen weak points.
Tools You Can Use for Network Security
Security tools are essential for monitoring your network, detecting threats, and providing defense against attacks. Some essential tools you can use include:
Antivirus Software: Protects computers and networks against malicious software.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Monitors network traffic and detects suspicious activities, taking preventative actions.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): These systems collect security events across your network, helping to analyze and detect threats.
These tools strengthen your defense mechanism against attacks and minimize security vulnerabilities.
What Are the Consequences of Neglecting Security?
Neglecting network security can have severe consequences for businesses. A cyberattack can result not only in financial losses but also in reputational damage. A business whose customer information is compromised may lose customer trust and suffer long-term business losses. Additionally, non-compliance with data security laws in many countries can lead to legal penalties. Therefore, ensuring network security is not only a technical necessity but also critical for business continuity.
Is a Firewall and Antivirus Enough?
Firewalls and antivirus software are fundamental tools for network security, but they are not enough on their own. While these tools can be effective against known threats, they may be insufficient against new and more sophisticated types of attacks. For instance, social engineering attacks or zero-day vulnerabilities may go undetected by these systems. Therefore, your security strategy should be multi-layered and include measures against various threats.
The Importance of Employee Training
Educated employees are one of the most important elements of cybersecurity. Trained employees are more resistant to social engineering attacks such as phishing. They can also detect suspicious activities early and respond more quickly to threats. Therefore, regular training programs and security awareness activities should be part of every business’s cybersecurity plan.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
With the widespread use of cloud technologies, cloud security has become a significant issue. To secure cloud systems, the following steps can be taken:
Data Encryption: Encrypting data stored in the cloud protects against unauthorized access. Authentication: Users with access to cloud platforms should be protected with multi-factor authentication methods. Regular Security Audits: Regularly auditing your cloud provider’s security practices helps identify vulnerabilities in advance.
Percentage of cyber attacks worldwide?
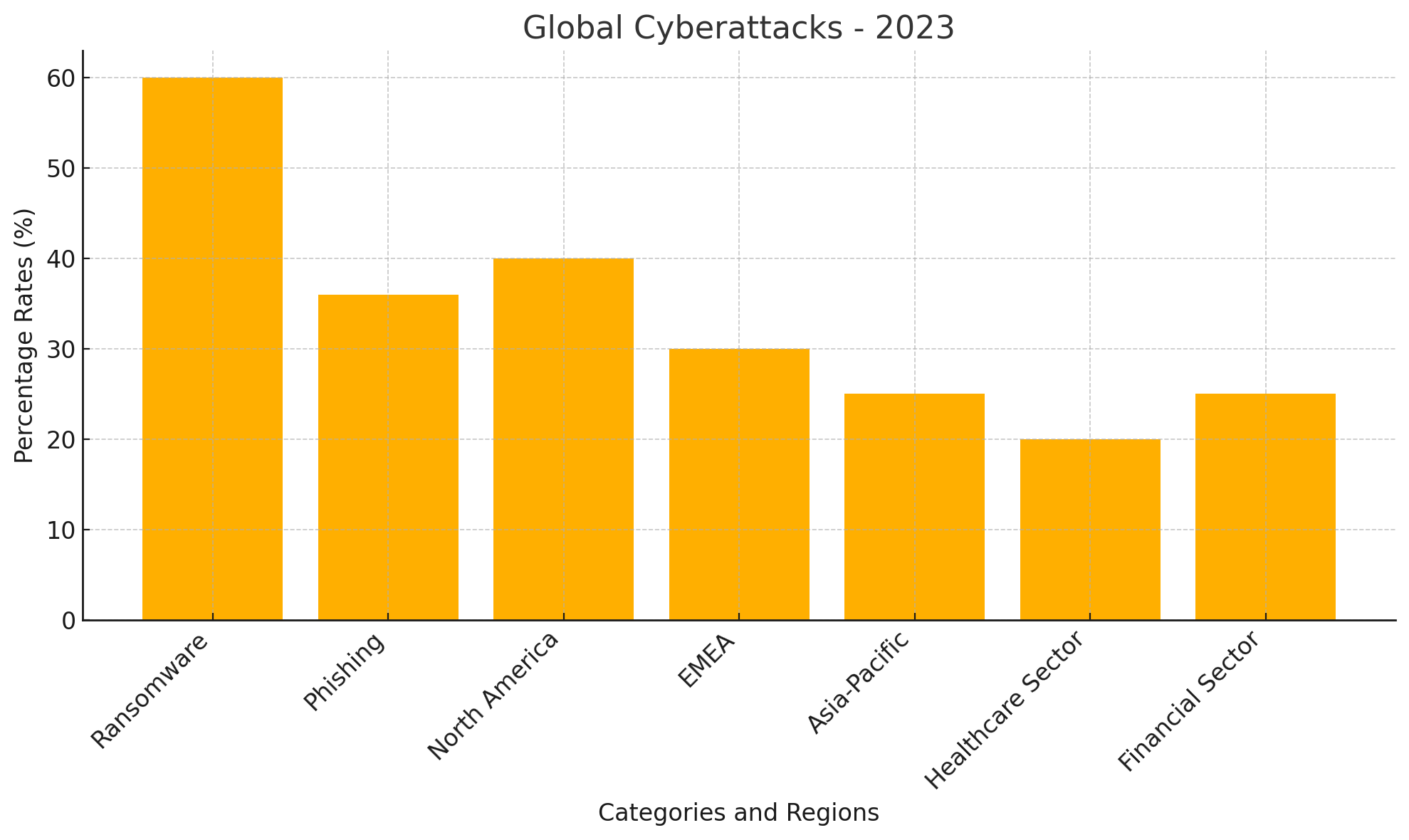
This data has been prepared in the light of the information obtained from https://www.verizon.com/. Cyberattacks are rapidly increasing worldwide, and these rates are detailed in various reports. The rate of cyberattacks varies by type, sector, and region. Between 2021 and 2023, ransomware attacks were among the fastest-growing types, with over 60% of attacks being ransomware-related in 2021. Phishing attacks saw a 36% increase in 2022, commonly aimed at stealing personal information. North America is the most affected region, accounting for 40% of all attacks, followed by Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) at 30%, and the Asia-Pacific region at 25%. The healthcare sector is one of the most targeted, accounting for 20% of attacks, while the financial sector faced 25%. Overall, cyberattacks have been growing by 30% to 40% annually, a trend that accelerated during the pandemic with the rise of remote work. Reports indicate that a cyberattack occurs every 39 seconds, with up to 95% of these incidents attributed to human error.
What are the best virus programs against cyber attacks worldwide?
Cyberattacks are increasing rapidly worldwide, and top antivirus programs are essential to defend against threats like malware, ransomware, phishing, and more. As of 2024, some of the best antivirus solutions include:
Bitdefender: Known for strong malware detection, Bitdefender offers ransomware protection, VPN, parental controls, and a password manager. It’s fast, has minimal impact on system performance, but some features like unlimited VPN require extra fees.
Norton 360: A comprehensive suite with powerful phishing and ransomware protection, Norton 360 includes cloud backup, a password manager, parental controls, and unlimited VPN. It’s highly effective, though slightly more expensive than others.
Kaspersky Total Security: Kaspersky provides top-tier malware detection, secure online payments, and parental controls. It has a low system impact and offers strong web protection, but there are some geopolitical concerns about its origins.
McAfee Total Protection: With phishing and ransomware protection, McAfee also includes a password manager, secure VPN, and multi-device support. Some features, however, come at additional cost.
Avast Premium Security: Avast offers malware protection, webcam privacy, and a password manager. It provides a robust free version, but its privacy policies have raised concerns in the past.
ESET NOD32 Antivirus: Known for its low system impact, ESET is effective against viruses, spyware, and phishing attacks, though it has fewer advanced features than competitors.

Trend Micro Maximum Security: Specializes in ransomware protection, Trend Micro also defends against identity theft and fraud. It has strong protection but can affect system performance.
Sophos Home: Ideal for families and multi-device setups, Sophos offers strong ransomware and web protection. It’s simple to use, with a solid free version, but advanced features require payment.

Windows Defender: Built into Windows, Defender provides basic malware protection, a firewall, and ransomware defense. It’s free and integrated, but lacks the advanced features of premium solutions.
Malwarebytes Premium: Malwarebytes excels in removing malware, ransomware, and spyware. It’s user-friendly, but compared to other solutions, it offers fewer advanced features.
In conclusion, while top solutions like Bitdefender, Norton 360, and Kaspersky lead the market with comprehensive protection, each antivirus has unique strengths. It’s important to choose one that best suits your specific needs and system requirements.
Ensuring network security has become a necessity for businesses. As threats like malware, phishing attacks, and ransomware grow more sophisticated by the day, taking effective precautions is crucial. A strong network security strategy should not only rely on technical tools but also be supported by employee awareness and training programs. By protecting your network with a multi-layered security approach, you can ensure business continuity and establish customer trust on a solid foundation.



