ABB robotics was founded in 1988 with the merger of Sweden-based ASEA and Switzerland-based BBC, world leaders in energy and automation technologies. ASEA was founded in Sweden in 1883 as a manufacturer of electric lighting and generators. ASEA revolutionised electricity transmission by installing the world’s first HVDC (high-voltage direct current) transmission line in 1954. BBC, founded in Switzerland in 1891, realised Europe’s first high-voltage electricity transmission. The merger of the two companies created a giant that offers innovative solutions in the fields of industrial automation and electrical energy.
One of the important milestones in ABB’s history was the consolidation of its leadership in robotics and automation solutions in the 1990s. In the 2000s, it focused on renewable energy and sustainable technologies and developed environmentally friendly solutions. During this period, ABB’s solar and wind energy projects made an impact around the world.
ABB continued its pioneering role in the era of digitalisation and industry 4.0. The company contributed to the digital transformation of the industry with advanced technologies such as smart grid technologies, energy storage solutions and AI-powered automation systems. Today, ABB works for a cleaner and greener future by offering solutions that increase energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprint in line with the principles of sustainability and innovation.
ABB’s vision is to use technology to improve human life and create a more sustainable world. The company operates in more than 100 countries around the world and maintains its leading position in industrial automation and electrical energy.
What Do ABB Robots Do?
ABB robots are designed to automate various industrial tasks, enhancing productivity and efficiency across multiple sectors. ABB robots perform a wide range of functions including welding, assembly, material handling, painting, and packaging. ABB’s extensive portfolio includes articulated robots, SCARA robots, delta robots, and collaborative robots (cobots), each tailored to specific industrial applications. For example, the ABB IRB 6640 is commonly used in automotive manufacturing for spot welding, while the FlexPicker delta robot excels in high-speed picking and packing operations.
Who is the CEO of ABB?
Morten Wierod is the President and CEO of ABB Ltd. He became CEO in August 2024 and has been a member of the Group Executive Committee since 2019. Wierod has a long history with ABB, holding various leadership positions in different divisions, including Electrification and Motion Business Areas. He holds a Master’s Degree in Electrical Engineering from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). His extensive experience within the company spans over two decades and multiple countries, emphasizing his expertise and leadership within the industry.

What Country is ABB Robots From?
ABB is headquartered in both Västerås, Sweden, and Zurich, Switzerland. The company was formed through a merger of Swedish and Swiss firms, and it has maintained significant operations in both countries. ABB’s dual heritage is reflected in its innovative engineering solutions and robust industrial presence across Europe and the globe.
How Much Do ABB Robots Cost?
The cost of ABB robots varies widely depending on the model, capabilities, and whether the unit is new or used. Prices for secondhand ABB robots range from $5,000 to $150,000. Newer models with advanced features and higher payload capacities generally fall on the higher end of the price spectrum. For instance, a used ABB robot with a payload capacity between 150 and 340 kg typically costs around $15,000. These prices reflect the robots’ extensive use in automotive production and other high-demand industrial applications.
What Companies Use ABB Robots?
ABB robots are utilized by a multitude of companies across different industries. Notable users include major automotive manufacturers such as BMW, Volkswagen, and Ford, which employ ABB robots for tasks like welding and assembly. In the electronics sector, companies like Apple and Samsung use ABB robots for precise assembly and packaging operations. ABB’s robots are also prevalent in the food and beverage industry, where they handle tasks such as packaging and palletizing.
Who Are ABB’s Competitors?
ABB faces competition from several other industrial robotics and automation companies. Key competitors include Japanese firms like Fanuc, Kawasaki, Mitsubishi Electric, and Yaskawa, as well as the German company KUKA. Additionally, American companies such as Rockwell Automation and Honeywell International are significant players in the automation and robotics market. These competitors offer a range of similar products and services, driving innovation and advancements in the industry.
What is the Fastest ABB Robot?
 The ABB IRB 6700 series, particularly known for its speed and accuracy, is among the fastest robots in ABB’s portfolio. These robots are designed for high-speed applications and are widely used in automotive manufacturing and other industries requiring rapid, precise movements. The IRB 6700 series builds on the legacy of the IRB 6000, which was noted for its speed and accuracy in spot welding.
The ABB IRB 6700 series, particularly known for its speed and accuracy, is among the fastest robots in ABB’s portfolio. These robots are designed for high-speed applications and are widely used in automotive manufacturing and other industries requiring rapid, precise movements. The IRB 6700 series builds on the legacy of the IRB 6000, which was noted for its speed and accuracy in spot welding.
Who is the Owner of ABB?
ABB is a publicly traded company with shares listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange in Zurich, the Nasdaq Nordic exchange in Sweden, and the OTC Markets Group’s pink sheets in the United States. The largest single shareholder is the Swedish investment company Investor AB, which is controlled by the Wallenberg family. Additionally, activist investor Cevian Capital holds a significant stake in ABB.
What is ABB Robotics’ Net Worth?
The company employs 109,390 people and has a market value (Enterprise valuation) of over $90 billion as of Jun 2024.
Where is ABB Ranked in the World Rankings?
ABB is ranked 498th in the Fortune Global 500 list as of 2024. The company has been on this prestigious list for 29 years, reflecting its consistent performance and significant global impact. ABB’s consistent ranking among the top global companies underlines its leadership in industrial automation, power technology and robotics.
ABB 2024 Report
ABB delivered strong financial performance, operational success and strategic progress in the second quarter of 2024. The company’s second quarter results were characterised by strong demand and a record high Operational EBITA margin.
ABB’s orders in the second quarter totalled $8.435 million, down 3% compared to the same period last year. However, the company’s revenues were $8,239 million, up 1%. Operating EBITA reached an all-time high of 19.0%. ABB’s earnings per share rose 22 per cent to $0.59 and cash flow from operating activities increased 40 per cent to $1,067 million.
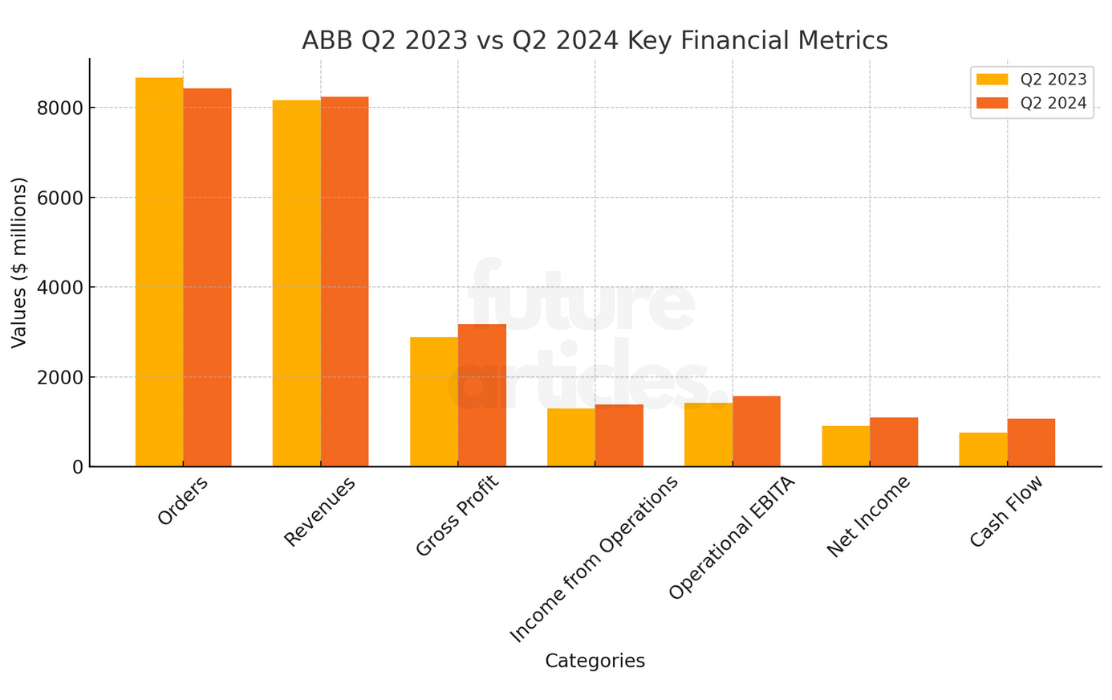
The Electrification segment was characterised by strong short-cycle business growth and solid project activity. Orders increased to $4,073 million, while revenues reached $3,809 million. The segment’s operating EBITA margin was a record 23.2 per cent. In the Motion segment, orders declined to $2,014 million, while revenues totalled $1,951 million. The Process Automation segment recorded an 8% increase in orders and 11% growth in revenues. The segment’s operational EBITA margin was 15.5 per cent.
ABB strengthened its commitment to sustainability and announced targets endorsed by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). The company plans to reduce absolute scope 1 and 2 CO₂ emissions by 80% by 2030 and 100% by 2050. It also aims to reduce scope 3 emissions by 25 per cent compared to the base year of 2022. ABB also continues to invest in innovative technologies such as the OmniCore control platform.
In the third quarter of the year, ABB forecasts an increase in comparable revenues and an Operational EBITA margin of around 18.5 per cent. For the full year 2024, revenue growth of around 5% and an Operational EBITA margin of around 18% are expected. ABB’s strong financial performance and strategic initiatives demonstrate the company’s commitment to growth and shareholder value creation.
ABB is a dominant force in the field of robotics, offering a wide range of advanced robots that cater to various industrial needs. Under the leadership of CEO Morten Wierod, ABB continues to innovate and expand its market presence, competing with other global leaders in the automation and robotics sectors. With a rich history and strong financial performance, ABB remains a key player in driving the future of industrial automation.


