When choosing storage for your computer, you will encounter two main options: Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Both serve the purpose of data storage but operate in fundamentally different ways and have their own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the differences between SSDs and HDDs can help you make an informed decision based on your storage needs, budget, and performance expectations.
How Do SSDs and HDDs Work?
SSDs and HDDs use different technologies. HDDs are traditional storage devices that use spinning magnetic disks (platters) to read and write data. An actuator arm with a read/write head moves across the disk to access or store information. This mechanical structure makes HDDs slower and more prone to physical wear and tear over time.
SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory to store data. They have no moving parts, allowing much faster data access and reducing the risk of mechanical failure. Data is stored electronically on NAND flash chips, which provides fast access and high durability.
In summary, HDDs rely on mechanical movements to read and write data, while SSDs perform the same task with electronic circuits. This fundamental difference leads to variations in speed, durability, and overall performance.
Which Has a Longer Lifespan: SSD or HDD?
In general, SSDs have a longer physical lifespan due to their lack of moving parts. The absence of mechanical components makes SSDs less sensitive to drops or vibrations, making them ideal for portable devices like laptops. However, SSDs have a limited number of write cycles due to the nature of flash memory. Advanced wear-leveling algorithms mitigate this limitation and extend the usable life of the SSD.
HDDs, being mechanical devices, are more prone to wear and tear over time. The spinning platters and moving heads can fail over time, especially in environments with physical shocks or extreme temperatures. However, HDDs are less affected by the number of read/write operations, making them suitable for long-term data storage where frequent access is not required.
In terms of durability, SSDs are physically more long-lasting, while HDDs may offer a longer lifespan for long-term data storage when used carefully.
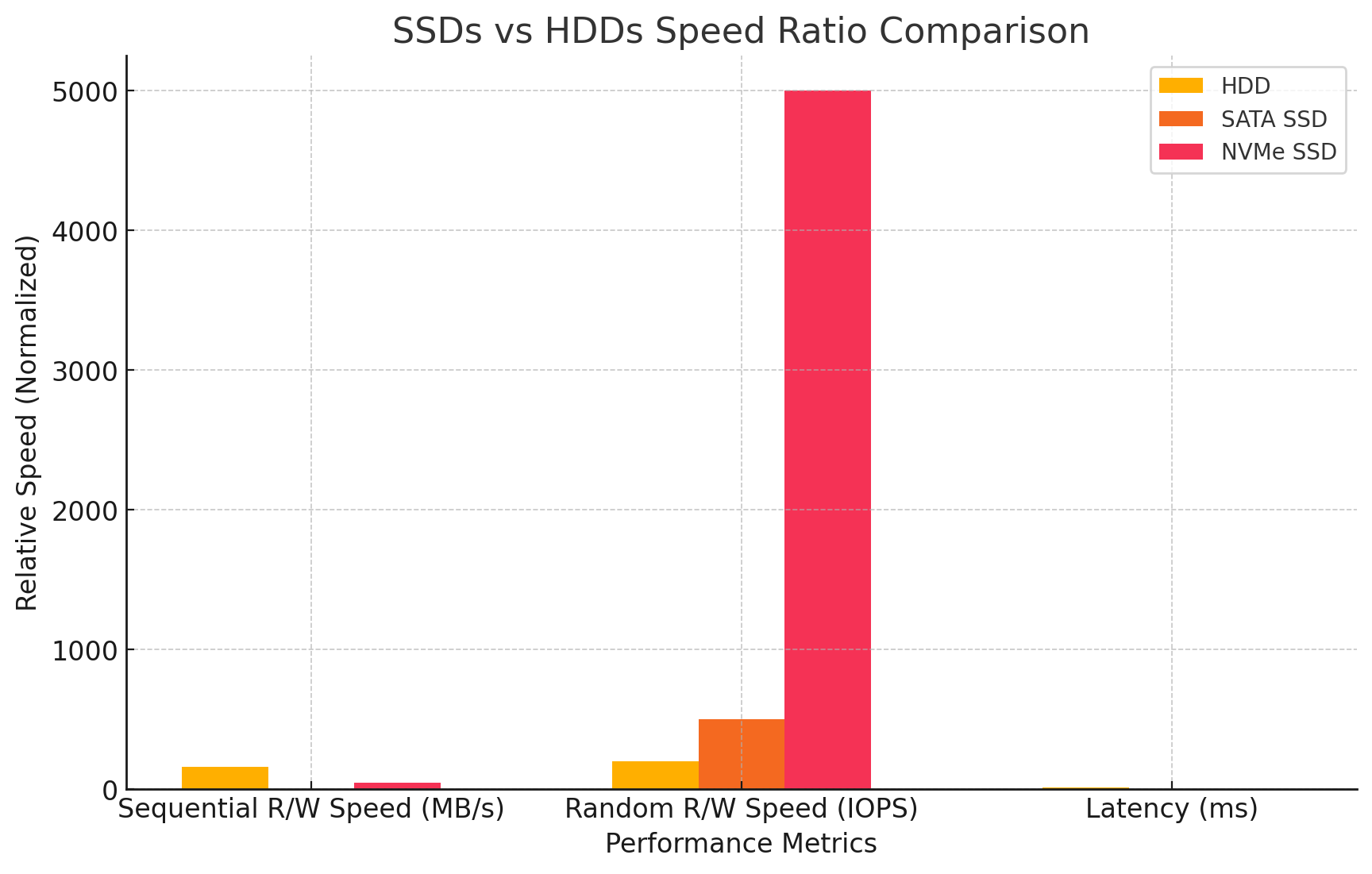
SSDs and HDDs Speed Ratio Comparison
Here is a graph comparing the speed ratios between HDDs, SATA SSDs, and NVMe SSDs based on sequential read/write speeds, random read/write speeds (IOPS), and latency. The values for SATA and NVMe SSDs are normalized against HDDs to highlight the relative performance improvements.
According to data from https://www.ibm.com/, SSDs and HDDs Speed Ratio Comparison is as follows.
Storage Capacity and Cost Differences
In terms of storage capacity, HDDs generally offer more storage space at a lower cost. High-capacity HDDs can reach 20 TB or more, making them ideal for users who need to store large amounts of data at an affordable price.
SSDs tend to be more expensive per gigabyte and typically offer capacities ranging from 256 GB to 8 TB for consumer models. Although prices are decreasing over time, SSDs are still more expensive than equivalent capacity HDDs. However, the investment in SSDs is often justified due to their superior performance and speed.
If cost and capacity are your priorities, HDDs are a more economical choice. If speed and performance are a priority, the higher cost of SSDs may be justifiable.
Energy Consumption and Noise Levels
SSDs are more energy-efficient compared to HDDs. Because they have no moving parts, SSDs consume less power, leading to longer battery life in laptops and lower energy costs in desktop systems. Additionally, the absence of mechanical movement means SSDs operate silently.
HDDs require more power to spin the platters and move the read/write heads. This mechanical movement generates noise and heat, making HDDs less suitable for quiet or energy-efficient environments.
Overall, SSDs are ideal for portable devices and quiet work environments due to their energy efficiency and silent operation.
Ideal Use Cases: When to Choose SSD and HDD?
The choice between SSD and HDD depends on the use case:
SSD: Ideal for applications requiring fast data access and quick boot times, such as operating systems, software applications, and games. They are also suitable for laptops and portable devices due to their durability and energy efficiency.
HDD: Best suited for long-term storage of large files, such as multimedia collections, backups, and archival data. They offer an economical solution for users seeking high-capacity storage without the need for fast data access.
The right storage choice depends on your needs. An SSD can significantly enhance system performance, while an HDD provides an economical solution for bulk data storage.
Impact on System Performance and Boot Times
SSDs significantly improve system performance and boot times. Due to their fast data access speeds, SSDs can reduce boot times to mere seconds and launch applications almost instantly. This makes SSDs an excellent option for improving overall system responsiveness.
HDDs, due to their mechanical nature, have slower data access times. Booting from an HDD can take significantly longer, and launching applications may result in delays.
If system performance and fast boot times are important to you, SSDs are a superior choice, providing a noticeable increase in speed compared to HDDs.
Data Security and Failure Rates
In terms of data security, SSDs are less prone to mechanical failures due to the absence of moving parts. However, recovering data from a failed SSD can be more difficult and costly compared to an HDD.
HDDs are more susceptible to physical damage, such as shocks or drops, which can lead to data loss. However, data recovery from HDDs is usually more feasible because the data is stored on magnetic platters.
For users concerned with physical data security and device durability, SSDs offer a safer option. However, it is important to make regular backups on both SSDs and HDDs to prevent data loss in case of failure.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Storage Technologies
The storage industry is shifting towards SSDs due to their superior speeds, durability, and decreasing costs. Innovations like NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs provide much faster data transfer speeds, making SSDs increasingly popular in both consumer and enterprise markets.
HDDs are evolving with higher capacities and advanced technologies like HAMR (Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording) to maintain their relevance for large-scale storage needs. However, the trend indicates a growing demand for SSDs as the primary storage solution in modern computing.
In summary, SSDs are the future of storage technology due to their performance advantages and decreasing costs, while HDDs continue to serve as a cost-effective solution for high-capacity storage needs.
Which brands of SSDs and HDDs are more preferred?
Preferred Brands for SSDs and HDDs:
Preferred brands for SSDs and HDDs can vary depending on factors such as product quality, performance, durability, and price. Here are some of the most preferred brands for SSDs and HDDs:
Preferred Brands for SSDs:
Samsung: Samsung is one of the most popular and reliable brands in the SSD market.Known for high-performance and durable SSDs.Models like the 860 Evo, 870 Evo, 970 Evo, and 980 Pro are particularly popular among users. Their NVMe SSDs also stand out for their high speeds.
Western Digital (WD): Western Digital offers both SATA and NVMe models in the SSD market. The WD Blue and WD Black series SSDs are preferred for their balance of performance and price. They also offer SSD products under the SanDisk brand.
Crucial: A subsidiary of Micron, Crucial is known for affordable and high-performance SSD solutions.
The MX500 and P5 series SSDs are notable for their durability and performance.
Kingston: Kingston is a reliable brand for both SATA and NVMe SSDs. Models like the A2000 and KC2500 are known for good performance and reasonable prices. They offer ideal options, especially for entry-level and mid-range users.
Seagate: Although Seagate is a well-known brand in the HDD sector, it also has a presence in the SSD market. They offer high-performance SSDs for gaming with their FireCuda series.
Intel: Intel offers durable and reliable SSD solutions, especially for corporate and professional users. Their Optane series provides high performance and low latency.
Preferred Brands for HDDs:
Western Digital (WD): One of the most popular and widespread brands in the HDD market. Series like WD Blue, WD Black, WD Red, and WD Purple are designed for different use scenarios. WD Blue is for everyday use, WD Black is performance-oriented, WD Red is optimized for NAS systems, and WD Purple is designed for surveillance systems.
Seagate: Seagate is a leading brand for high-capacity and high-performance HDDs. Known for product lines like Barracuda, IronWolf, and SkyHawk. The Barracuda series is popular for general use, while the IronWolf series is optimized for NAS.
Toshiba: Toshiba is known for affordable and reliable HDD solutions. Their P300, X300, and N300 series HDDs are preferred for general use, performance-oriented tasks, and NAS systems, respectively.
HGST (Hitachi Global Storage Technologies): HGST offers enterprise-level HDDs with high durability. Preferred for data centers and professional use. The Ultrastar series from HGST provides high reliability and performance.
Samsung: Although Samsung is not as active in the HDD market as it once was, some users still prefer their older models.
The preferred brands can vary based on user needs, budgets, and use scenarios. For instance, those looking for high performance and durability might prefer brands like Samsung or Crucial, while those needing large storage capacity at a reasonable price might choose WD or Seagate.